

In Canada, they may be members of the Canadian Association of Genetic Counsellors ( The National Society of Genetic Counselors defines genetic counselling as “the process of helping people understand and adapt to the medical, psychological and familial implications of genetic contributions to disease. Genetic counsellors are health professionals with specialized training and experience in providing genetic counselling. Current short-read genome sequencing can reliably detect sequence, structural and copy number variations, both within and outside of exons, as well as clinically relevant short tandem repeats, pseudogenes and mitochondrial DNA variation. Genome sequencing: this approach offers myriad advantages as a single comprehensive test. Next-generation sequencing gene panel test: a targeted test focusing on a predefined list of genes that typically detects only exonic sequence-level variants and exon-level deletions or duplications in those genes.Įxome sequencing: a genome-wide test that typically detects only exonic sequence-level variants, a subset of exon-level deletions or duplications, and a subset of copy number variations.

Overview of selected clinical genetic test modalities 6įor patients with phenotypes with known genetic heterogeneity, the following tests are commonly employed in clinical practice:Ĭhromosomal microarray analysis: a genome-wide test that typically detects only copy number variations (i.e., chromosome imbalances). These variants are filtered and reviewed by a genome analyst to identify 1 or more that might be causal for the observed clinical presentation. Variants (differences) from that reference are annotated using sophisticated bioinformatics tools and large-scale databases of genomic variation. The average number of reads covering a given genomic position (the “read depth”) is typically 30–40. DNA is fragmented into small pieces and run on a high-throughput sequencing machine to generate millions of “nucleotide reads.” Reads are aligned to a reference genome, like puzzle pieces being assembled by looking at the image pictured on the box. Samples from biological parents are often sequenced at the same time to give additional context regarding inheritance. After appropriate pretest counselling, including review of possible results, a DNA sample is obtained from the patient, usually via a blood draw.
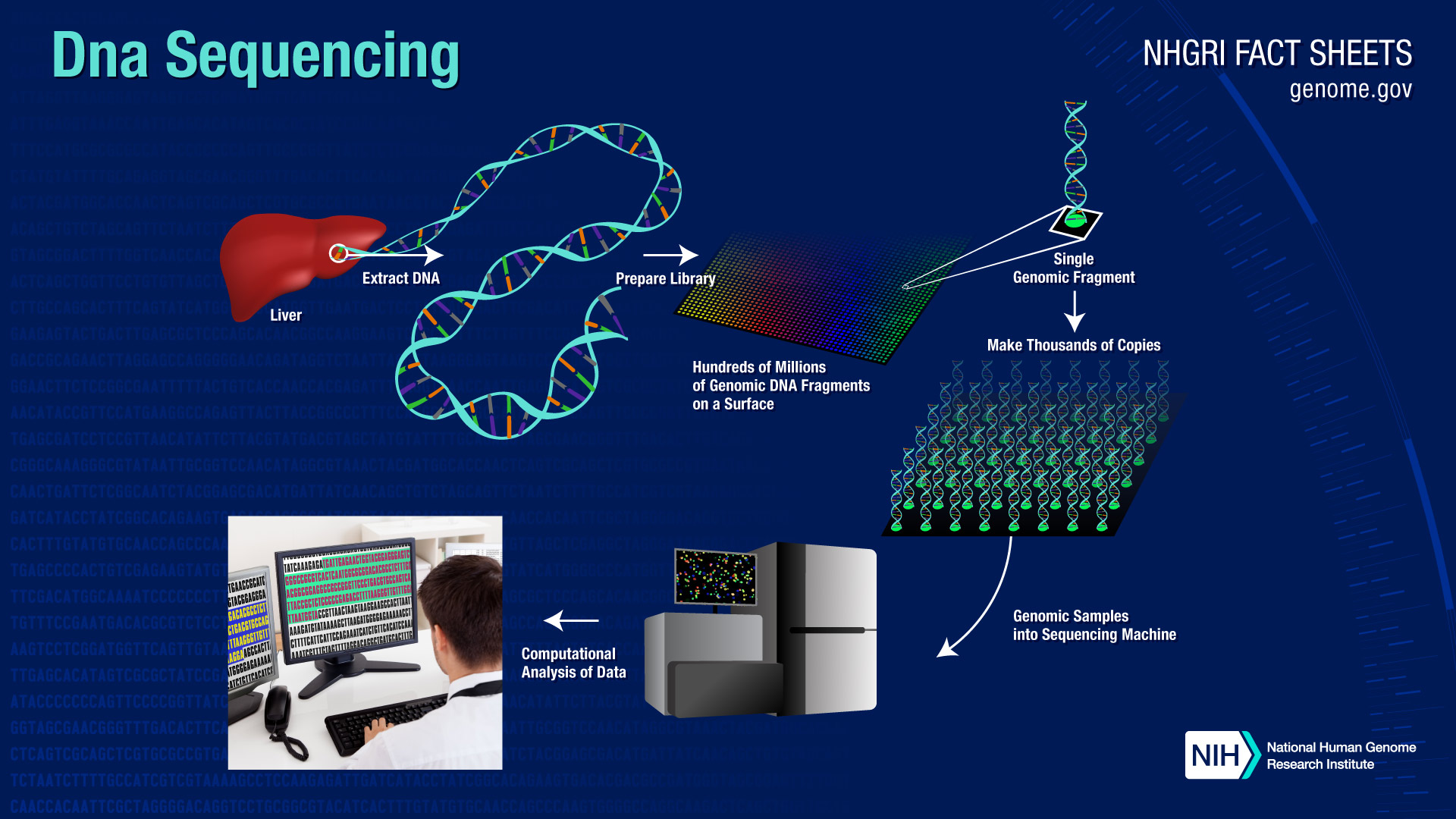
Note: Variants in the KDM6A gene are linked to Kabuki syndrome. Middle panel was adapted from “Whole Genome Sequencing” by (2021) retrieved from. 5 Starting in 2021, genome sequencing is being performed as a clinical genetic test in Ontario, Canada. 3, 4 Genome sequencing is being integrated into health care systems internationally, most notably in the United Kingdom. 1 – 3 Sequencing an entire human genome (about 3.2 billion nucleotides) is now possible to complete in days to weeks, and at a similar cost to some advanced imaging tests or to a brief admission to hospital. Genetic testing of patient constitutional DNA (i.e., their genome) is increasingly performed in medical practice.

Test indications include suspected genetic disorders in children and adults for whom a targeted genetic testing approach is likely to be low yield or has already failed.Īnalytic validity, diagnostic yield and clinical utility are similar or superior to other clinical genetic tests, such as exome sequencing, chromosomal microarray analysis and next-generation sequencing gene panel tests.Īppropriate adoption of genome sequencing as a molecular diagnostic test in Canada would be facilitated by a cohesive national strategy for genomic medicine. Genome sequencing is a comprehensive genetic test that is being integrated into health care systems internationally.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
